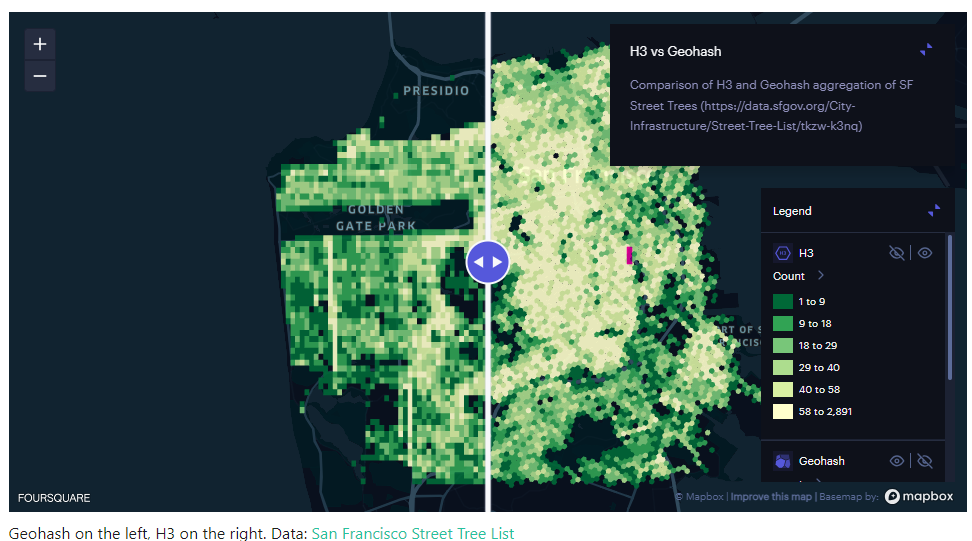
Geohash vs H3: Which Geospatial Indexing System Should I Use?
For years, the go-to geospatial indexing system has been Geohash. However, a relative new contender has emerged, challenging the status quo – H3. So should you use Geohash or H3?
Here, we’ll explore the differences between Geohash and H3, to help you decide which geospatial indexing system best suits your needs.
Geohash: A Familiar Friend
Geohash is a widely-used geocoding system that encodes geographic coordinates into a short string of letters and numbers. It divides the world into a grid of rectangles, each with a unique Geohash code. The longer the Geohash string, the more precise the location it represents.
H3: The Challenger
H3, on the other hand, is a relatively newer geospatial indexing system that’s gaining traction for its unique approach. Developed by ride-sharing company Uber, H3 uses a hexagonal grid to represent the Earth’s surface. Each hexagon is assigned a unique H3 index, offering a different perspective on geospatial indexing compared to Geohash.
Comparing Geohash and H3
We delve into the main differences between Geohash and H3 on a number of measures.
Precision
- Geohash: Precision varies based on the length of the code. Longer codes are more precise, but this increases storage and complexity.
- H3: H3 offers consistent precision regardless of location. Hexagons can be further subdivided for more precision, ensuring uniformity.
Spatial Relationships
- Geohash: Geohash’s rectangular grid can struggle to represent spatial relationships accurately, especially near the poles (it should be noted that realistically, this is not going to be an issue in most use cases).
- H3: H3’s hexagonal grid provides better spatial relationships, making it ideal for applications like ride-sharing services and navigation.
Support and Ease of Use
- Geohash: Geohash is simple and widely adopted, making it easier to find resources and libraries for various programming languages.
- H3: While H3 is gaining popularity, it may not have the same level of community support and resources as Geohash.
Applications
- Geohash: Geohash is well-suited for applications that require basic geospatial indexing, such as location-based search or geofencing.
- H3: H3 shines in complex applications like urban planning, logistics, and ride-sharing due to its consistent precision and better spatial relationships.
Scalability
- Geohash: As Geohash codes get longer for more precision, storage and indexing can become inefficient.
- H3: H3 scales more efficiently because it maintains uniform precision, regardless of location.
Source: H3
Geohash or H3: Choosing the right system
When it comes down to the choice between Geohash and H3, it really depends on your specific needs:
- If you require a straightforward geospatial indexing system for basic applications, Geohash is a reliable choice with extensive community support.
- On the other hand, if you’re dealing with complex spatial relationships, require consistent precision, or are working on innovative projects like urban planning or ride-sharing services, H3 offers a more promising solution. In the real estate context, it can be useful in urban planning, geofencing, spatial analysis, property market analysis.
Geospatial indexing is a fundamental technique used to manage and organise geographic or location-based data efficiently, in order to make data-based decisions or enhance applications.
Geohash is the old guard, tried and tested, while H3 is the newcomer with fresh ideas and uniform precision.
As we can see, both Geohash and H3 have their merits. However, the ultimate decision of which system to use should be based on the requirements of your project.
Snowflake releases H3 functionality
Snowflake provides SQL functions that enable you to use H3 with GEOGRAPHY objects.
This preview feature is now available to all accounts.