Understanding Auction Clearance Rates: Why Do Calculations Differ?
Auction clearance rates can serve as a barometer of Australia’s real estate market strength, particularly across its major cities.
These rates are generally a superficial gauge of market strength, because private treaty is still the most common means of property sale in some cities. Nevertheless, property predictions can be drawn when auction clearance rates are analysed alongside other factors and data points.
Clearance rates for Australia’s major real estate markets can be helpful for proptechs who leverage data, analytics, and technology to advance various aspects of the real estate industry.
What Is An Auction Clearance Rate?
The auction clearance rate typically represents the percentage of properties that sold on its advertised auction date in a specific market versus the number of properties that didn’t sell during a particular time frame (typically a week or month).
How Are Auction Clearance Rates Calculated?
There are variations in how clearance rates are calculated and reported, so it’s important to consider this and understand your data provider’s calculations. The variance in calculations means these metrics offer different views and are not interchangeable.
Variations to the Calculation | Calculation | Calculation (%) |
| Basic calculation | Percentage of properties sold on auction date during a particular period (week or month) |  |
| Includes properties sold prior to and during auction | Percentage of properties sold prior to plus on auction date during a particular period (week or month) |  |
| Includes properties sold prior to, during and after auction | Percentage of properties sold prior to auction plus on auction date plus after auction date during a particular period (week or month) | 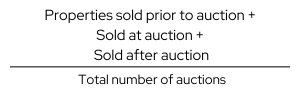 |
What Do Auction Clearance Rates Tell Us?
Auction clearance rates are a crucial market indicator of real estate activity by gauging the numbers of buyers and sellers in a specific market during a certain time frame.
Generally, higher auction clearance rates indicate a higher buyer demand for property in that market, limited supply of available properties and/or with an increased likelihood of rising price, i.e. a hot market for sellers.
Conversely, low auction clearance rates indicates weak buyer demand, possible over-supply of properties and chance of reduced prices which is more favourable to buyers.
In Sydney and Melbourne, a clearance rate above 70% signals a seller’s market, below 60% suggests a buyer’s market, and 60-70% indicates balance.
But the true significance of auction clearance rates lies in its contextual analysis alongside factors such as listing numbers, days on market, withdrawn auctions, fluctuations and regional disparities.
By tracking these rates alongside additional metrics, analysts can anticipate market direction, and measure buyer and seller confidence.
Where Can I Find Clearance Rates For Australia’s Capital Cities?
Auction clearance rates in Australia are reported on a weekly basis.
Some organisations collect data from sales agents and aggregate the data by city and region, such as:
Some news outlets, auction houses and real estate agencies may also publish auction clearance rates for specific regions. Industry reports and analyses related to real estate may also compile this data to provide a comprehensive view into trends.
How Important Are Auction Clearance Rates?
For anyone involved in or impacted by the real estate market, auction clearance rates are an important indicator of demand levels, market sentiment, and potential shifts in property values. But when comparing available data, its crucial to understand the methodology behind the calculations of auction clearance rates.
Auction clearance rates should be used as part of a comprehensive analysis alongside other property data, localised research, and broader market factors. While auction clearance rates offer valuable insights into the direction of the property market, they are just one of many factors to consider, and a holistic approach incorporating various data points is recommended for a thorough understanding of market conditions.
How Might Auction Clearance Rates Be Used By Proptechs?
While not exhaustive, these are a few examples of how auction clearance rates might be used by proptechs and businesses working with real estate data.
- By analysing clearance rates and buyer demand, price trends can be used to gauge competitiveness of the market. These could all be incorporated into tool development or software development, it could be used to optimise platform features, or to guide content creation to engage users.
- Combining this information with localised data for property investment, integrating clearance rate data into risk assessment models could allow for more informed investment decisions.
- Property valuation models could be enhanced with the use of real-time clearance rate data which provides more accurate and dynamic property valuations in areas of high auction activity.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to receive the latest blogs and data listings direct to your inbox.






